TOLERANCES, DIMENSIONS AND COMPENSATION FOR YOUR PROJECTS IN PHOTOETCHING, PRECISION CASTING AND LASER CUTTING.
How do you design a component in photoetching or laser cutting? What tolerances are obtained with investment casting? What about electroforming?
On this page you will find the main indications, the minimum dimensions, the compensations, and the tolerances for the different technologies, but write to our
Choose the technology...
-
photoetching, cuts and engravings from plates up to 2 mm
-
investment casting, three-dimensional components of any shape
-
electroforming, logos and very fine and self-adhesive decorations
-
laser cutting, details cut from plates up to 4 mm
Choose the thickness or size
In photoetching or chemical milling it is possible to obtain flat components engraved and cut from plates from 0.05 up to 2 mm thick. With laser cutting it is possible to cut higher thicknesses but without engraved areas.
In investment casting, the minimum obtainable thickness is 0.5 mm, and up to a maximum of 8 mm.
Electroforming is suitable for obtaining flat and glossy parts with a thickness of 0.05 / 0.10 mm.
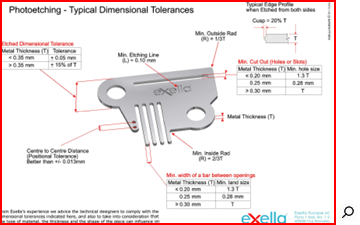
Photoetching (chemical milling)
-
standard tolerances , standard dimensional and center distance tolerances (distance between the center of the holes), thickness tolerance of the slab and flatness.
- minimun size , indicates the minimum width of an incision line, minimum width of a line in relief, minimum cut and minimum line of material between two cuts, and finally the smallest achievable exterior and interior radii.
- offset design , during machining the dimensions of the components tend to shrink slightly, and it is necessary to provide an external compensation offset and a reduction of the holes. However for decorative components and for thicknesses lower than 0.40mm, this operation is not necessary.
- cutting profile , photoetching has a typical cusp cutting profile, more evident on components with thicknesses of 0.70 mm, which may require subsequent chemical or physical tumbling.
- metal lamination , the fold lines must be perpendicular to the lamination direction of the plate. Otherwise you run the risk of cracking at the corners, especially with harder steels.
Lost wax casting (investment casting)
-
standard tolerances , select the thickness of the component and find the standard dimensional tolerances and center distance (distance between the center of the holes), flatness and parallelism and angular tolerance.
minimun size , indicates the minimum width of an incision line, minimum width of a line in relief, minimum hole and minimum obtainable thickness. - metal shrinkage , the shrinkage of holes and dimensions during the investment casting process, requires a compensation (surcharge) of approximately 1.5% or 2%. For models designed in 3D, this operation is applied directly by our technical office.
- thickness, maximum thickness obtainable in investment casting
-
surface roughness , the surface condition of the finished component, if reproduced from a 3D drawing or from a perfectly smooth physical sample.
Laser cut (laser cut)
-
standard tolerances , standard dimensional and center distance tolerances (distance between the center of the holes), thickness tolerance of the slab and flatness.
- minimun size , indicates the minimum cut and minimum line of material between two cuts, and the smallest obtainable external and internal radii.
- offset design , during machining the dimensions of the components tend to shrink slightly, and it is necessary to provide an external compensation offset and a reduction of the holes. However for decorative components, this step is not necessary.
- metal lamination , the fold lines must be perpendicular to the lamination direction of the plate. Otherwise you run the risk of cracking at the corners, especially with harder steels.
Electroforming (electroforming)
-
standard tolerances , standard dimensional and center distance tolerances (distance between the center of the holes), thickness tolerance of the slab and flatness.
- minimun size , indicates the minimum cut and minimum line of material between two cuts, and the smallest obtainable external and internal radii.
Some questions?